IBM Data & AI
To thrive in this age of the unexpected, companies must leverage data, AI and machine learning (ML) to create customer loyalty, automate business processes, and innovate future ideas. But the demand for data has outpaced our ability to solve our existing data problems – the copy and paste method has only made things worse.
Companies need a new architecture to become truly data-driven and put AI to work – a data fabric. With a data fabric approach, companies can connect the right people, to the right data, at the right time to promote agility, predict outcomes, and personalize experiences.
Solutions
| Provide Access with Data Fabric | Promote Agility with Data Management |
| Predict outcome with Business Analytics | Personalize Experience with Customer Care |
Data Fabric
What is a data fabric?
A data fabric is an architectural approach to simplify data access in an organization to facilitate self-service data consumption. This architecture is agnostic to data environments, processes, utility, and geography, all while integrating end-to-end data-management capabilities. A data fabric automates data discovery, governance, and consumption, enabling enterprises to use data to maximize their value chain. With a data fabric, enterprises elevate the value of their data by providing the right data, at the right time, regardless of where it resides.
Challenge(s) of Data Today?
Data is an integral element of digital transformation for enterprises. But as organizations seek to leverage their data, they encounter challenges resulting from diverse data sources, types, structures, environments, and platforms. This multidimensional data predicament is further complicated when organizations adopt hybrid and multi- cloud architectures. For many enterprises today, operational data has largely remained siloed and hidden, leading to an enormous amount of dark data.
Take the example of a North American energy company that sought to reinvent themselves as a data-driven organization—to become a company where data science capabilities were readily accessible across multiple business units. They soon realized that their digital transformation was hampered by siloed data, inconsistent tools, and various skill levels, all of which caused critical gaps between data competencies. The problem they faced was not unique to their business; in fact, it is a common consequence of data landscapes that have outgrown their data management architectures. What ultimately brought the energy company back onto a successful path for digital transformation was the employment of a new data architecture concept known as data fabric.
What exactly is a data fabric, how does it differ from previous architectures, what can it achieve for businesses, and what is IBM’s role in implementing it? This white paper will answer those questions.
In the past, organizations have attempted to address data access problems either through point-to-point integration or introduction of data hubs. Neither of those are suitable when data is highly distributed and siloed. Point-to-point integrations add exponential cost for any additional end point that needs to be connected, meaning this is a non-scalable approach.
Data hubs allow for easier integration of applications and sources but exacerbate the cost and complexity to maintain quality and trust of data within the hub. The data fabric is an emerging architecture that aims to address the data challenges arising out of a hybrid data landscape.
Its fundamental idea is to strike a balance between decentralization and globalization by acting as the virtual connective tissue between data endpoints. Through technologies such as automation and augmentation of integration, federated governance as well as activation of metadata, a data fabric architecture enables dynamic and intelligent data orchestration across a distributed landscape, creating a network of instantly available information to power a business.
A data fabric is agnostic to deployment platforms, data processes, geographical locations, and architectural approach. It facilitates the use of data as an enterprise asset. A data fabric ensures your various kinds of data can be successfully combined, accessed, and governed both efficiently and effectively.
Capabilities and principles of a data fabric.
The core of the data fabric architecture is a data management platform that enables the full breadth of integrated data management capabilities including discovery, governance, curation, and orchestration.
However, a data fabric advances and evolves from traditional data management concepts such as DataOps, which only focuses on establishing practices, to increase the level of data operationalization. It is built upon a distributed architecture and advanced technology able to address the needs that arise from extreme diversity and distribution of data assets.
Data fabric architecture delivers instant benefits.
A data fabric could be logically divided into four capabilities (or components): Knowledge, insights, and semantics –Provides a data marketplace and shopping experience –Automatically enriches discovered data assets with knowledge and semantics, allowing consumers to find and understand the data
Unified governance and compliance –Allow local management and governance of metadata but supports a global unified view and policy enforcement –Automatically applies policies
Intelligent integration –Accelerates a data engineer’s tasks through automated flow and pipeline creation across distributed data sources –Enables self-service ingestion and data access over any data with local and global deep enforcement of data protection policies
Automatically determines best fit execution through optimized workload distribution and self-tuning and correction of schema drifts Orchestration and lifecycle –Enables the composition, testing, operation, and monitoring of data pipelines –Infuses AI capabilities in the data lifecycle to automate tasks, self- tune, self-heal and detect source data changes, all of which facilitates automated updates.
Orchestration and lifecycle –Enable the composition, testing, operation and monitoring of data pipelines –Infuses AI capabilities in the data lifecycle to automate tasks, self- tune, self-heal and detect source data changes, all of which facilitates automated updates
Why IBM?
Holistic view across a distributed data landscape
Intelligently integrate and unify data across hybrid and multi-cloud to deliver trusted data and speed time to business value.
Automate and enforce policies and rules automatically and consistently across data on any cloud with increased visibility and collaboration while reducing compliance risks.
Consolidate data management tools and minimize data duplication for faster access to higher quality, more complete data that renders deeper insights.
Business benefits of a data fabric
Data only delivers business value when it is contextualized and becomes accessible by any user or application in the organization. When implemented correctly, a data fabric helps ensure those values are available throughout the organization in the most efficient and automated way possible. As such, the fabric has three key benefits:
1. Enable self-service data consumption and collaboration.
2. Automate governance, protection, and security; enabled by active metadata.
3. Automate data engineering tasks and augment data integration across hybrid cloud resources.
Enable self-service data consumption and collaboration
By integrating data from multiple sources and analysing a larger fraction of the enormous amount of data generated daily, organizations gain better insights and respond more quickly to changing business demands. A data fabric rapidly delivers data into the hands of those who need it. Self-service enables the organization to find appropriate data quicker and spend more time using that data to provide tangible insights.
Benefits of data fabric for self-service data consumption:– Business users have a single point of access to find, understand, shape and consume data throughout the organization.– A centralized data governance and lineage help users understand what the data means, where it comes from, and how it is related to other assets.– Extensive and customizable metadata management scales easily and is accessible via APIs.– Self-service access to trusted and governed data enables line-of-business collaboration with other users. A Forrester Total Economic Impact study1 revealed that these capabilities can mean: USD 5.8M in benefits 459% ROI Automate governance, data protection and security; enabled by active metadata A distributed active governance layer for all data initiatives reduces compliance and regulatory risks by providing trust and transparency.
It enables automatic policy enforcement for any data access, providing a high level of data protection and compliance. Utilizing AI and machine learning technologies allows data fabric users to increase their level of automation, for example automatically extracting data governance rules based on language and definitions in regulatory documents.
This allows organizations to apply industry specific governance rules in a matter of minutes to help avoid costly fines and ensure ethical use of data wherever it resides. Benefits of a data fabric for governed virtualization: – Agility, security, and productivity is increased for data engineers, data scientists, and business analysts. – Multiple global data sources appear as one database. – New, industry-leading discovery of personally identifiable information (PII) and critical data elements is possible at massive scale.
These capabilities can mean:
USD 2.4M in benefits1- 430% performance improvement
Automate data engineering tasks and augment data integration Advanced data engineering means that virtually any data access or delivery process is automated and not requiring any tedious or error-prone coding process.
Augmentation of integration utilizes metadata data to optimize the data delivery and access. Benefits of a data fabric for data engineering and integration:– Automatically optimized data integration helps accelerate data delivery.– Automatic workload balancing, and elastic scaling means jobs are ready for any environment and any data volume.– Resiliency and CI/CD automation are built in.– The automated process for capturing changes in real time supports delivery of quality data for business processes.– Machine learning can automate and extend custom data discovery, classification and curation processes, leading to faster time-to-value.– Continuous analysis can be automatically performed in real time, wherever data lives.
Results from a leading retailer show:
60X acceleration in data – delivery time 20X faster customer affinity analyses 5 IBM Hybrid
Data fabric architecture delivers instant benefits.
Provide a 360° view of your customers
Achieve a single, trusted, and comprehensive view of customers by connecting data across all sources in your organization. Minimize risk, increase precision, and improve decision-making speed by centrally managing master data. The single view enables business users within enterprises to extract key insights that facilitate the delivery of a superior customer experience.
Also, a comprehensive view helps position products and services to meet customers’ needs.
Benefits of a data fabric for a 360° customer view:
- Compile a customized and trusted customer view.
- Enable workflow capabilities to implement governance policies and processes.
- Operationalize master data for deeper analysis and enhanced insights.
- Manage your customer relationships and hierarchies and get more accurate reporting.
Support trusted AI
Leverage a data fabric to capture the AI lifecycle to enable greater visibility and automate documentation of the lifecycle. Also, determine which enterprise policies will be enforced during the development and deployment lifecycle.
Benefits of a data fabric for trust in AI:
- Enable the automatic monitoring of models and automatically re-train when applicable.
- Leverage governance rules to automate the control of the model lifecycle.
- Utilize automated monitoring to identify bias, drift, and ensure fairness.
- Make smart recommendations.
How IBM delivers a data fabric
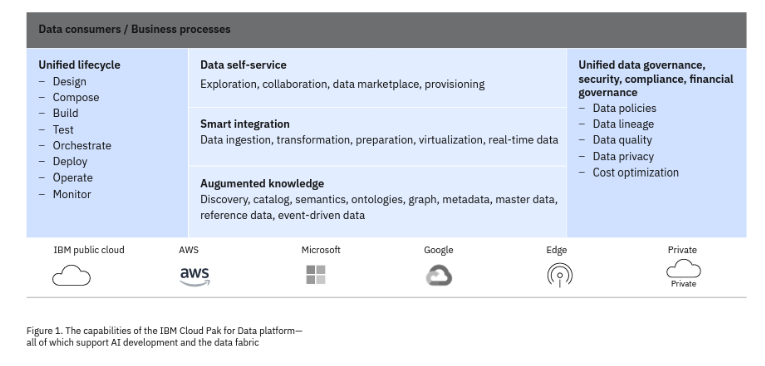
IBM Cloud Pak® for Data makes this concept of a data fabric possible. IBM Cloud Pak for Data is an insight platform that simplifies and automates data collection, organization and analysis of data and accelerates the infusion of AI throughout your business.
With its capabilities to connect data everywhere; run workloads anywhere; and to build, deploy and manage AI at scale in hybrid cloud environments, IBM Cloud Pak for Data is the enabler for a business digital transformation.
The platform delivers seamless integration across a hybrid enterprise for:
- IBM Cloud Pak for Data services
- External applications and data sources
- Advanced AI-based capabilities for data management and governance
This foundation makes curated data available to consumers with the optimum balance of cost, performance, compliance, and with the intelligence to orchestrate and optimize data processing based on workloads, data locality, and data policies.
IBM Cloud Pak for Data leverages the following capabilities to deliver the business-ready data a data fabric demands. All these capabilities play a part in supporting the data fabric architecture.
- Metadata-based knowledge core
Facilitates the discovery of data sources and catalogues; enriches data assets; and performs analysis to extract insight for more automation using AI. The knowledge core is used to power the marketplace with semantic search.
- Self-service data marketplace
The next-generation data catalog that helps data consumers, such as business analysts, retrieve data from across the data landscape of the enterprise.
- Smart integration
Enables data consumption by extracting, virtualizing, transforming, and streaming data. It is integrated with the knowledge core to automate data integration and has the intelligence to decide which integration approach is best suited based on workloads and data policies. It can also be used for data preparation as part of data engineering workloads or to create data products. Finally, it provides the ability to publish updates to data products.
- Governance
Catalogs and curates’ metadata, defines data policies for privacy, curates’ data, captures data lineage, and performs other tasks related to security and compliance. This layer understands the data format (for example, structured vs. unstructured) and data significance (for example, public vs. protected) and applies the correct policies to each bit of data and each prospective user. Instead of applying standards and rules to data manually, this integrated platform capability means they can be applied at the organizational level and propagate throughout the various data resources as needed. Analytic models in different tools can talk to one another; data policy enforcement at the granular level can be largely automated.
- Unified development and operations
Enables a unified lifecycle to configure and run all the aspects of the data platform in production.
Data fabric in action
The best way to understand the value of a data fabric is to see the business benefits that actual organizations have achieved through implementing a data fabric on top of an insight platform.
Energy company
The challenges section at the beginning of this white paper introduced the case of a North American energy company undergoing a digital transformation. This customer engaged with IBM who implemented a data fabric architecture based on IBM Cloud Pak for Data.
With a flexible and integrated data fabric in place, the company was able to implement a range of important data projects across different units, including:
– eMobility
– Gas operations document discovery, including handwriting extraction
– Electric customer segmentation and load forecasting
– Asset management
– COVID-19 load impacts
– Return-to-work risk model
With a data fabric, this organization can:
– Provide multiple business units with direct data access via a self-service insight platform.
– Use fit-for-purpose compute capacity to efficiently run models on billions of rows of data.
– Collaboratively develop models and easily deploy those models to infuse insight throughout the company.
Reducing movement and improving oversight
A large industrial service provider improved data governance and facilitated regulatory compliance.
This organization struggled to move large amounts of data to their cloud-based data lake. They had the twin requirements to apply a strong layer of governance to every instance of data access and to determine data quality before providing business user access. By implementing a data fabric built on IBM Cloud Pak for Data this organization made enormous improvements to their data governance, data compliance and data transformation processes.
With a data fabric in place, they can provide business users with easy, secured access to hundreds of data sources in their cloud-based data lake and on-premises SAP data sources. They are also leveraging industry regulatory accelerator tools to scan data sources for possible PII data that would be subject to GDPR and CCPA regulation.
Automatic data flagging helps identify any data sources that need to be managed for PII handling both on-premises and on the cloud. With better access and quicker PII screening business users can mine relevant data for important insights without long waits for data access or running the risk of exposing protected data.
With a data fabric, this organization can:
– Ensure proper data governance, while simultaneously leveraging data from across the company.
– Get trusted data and reduce the amount of data preparation.
– Assist in compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Figure 1. The capabilities of the IBM Cloud Pak for Data platform— all which support AI development and the data fabric Google U